Battery storage is a technology that stores electrical energy in the form of chemical energy within batteries for later use. It plays a critical role in modern energy systems by addressing the intermittency of renewable energy sources like solar and wind, improving grid stability, and providing backup power during outages.
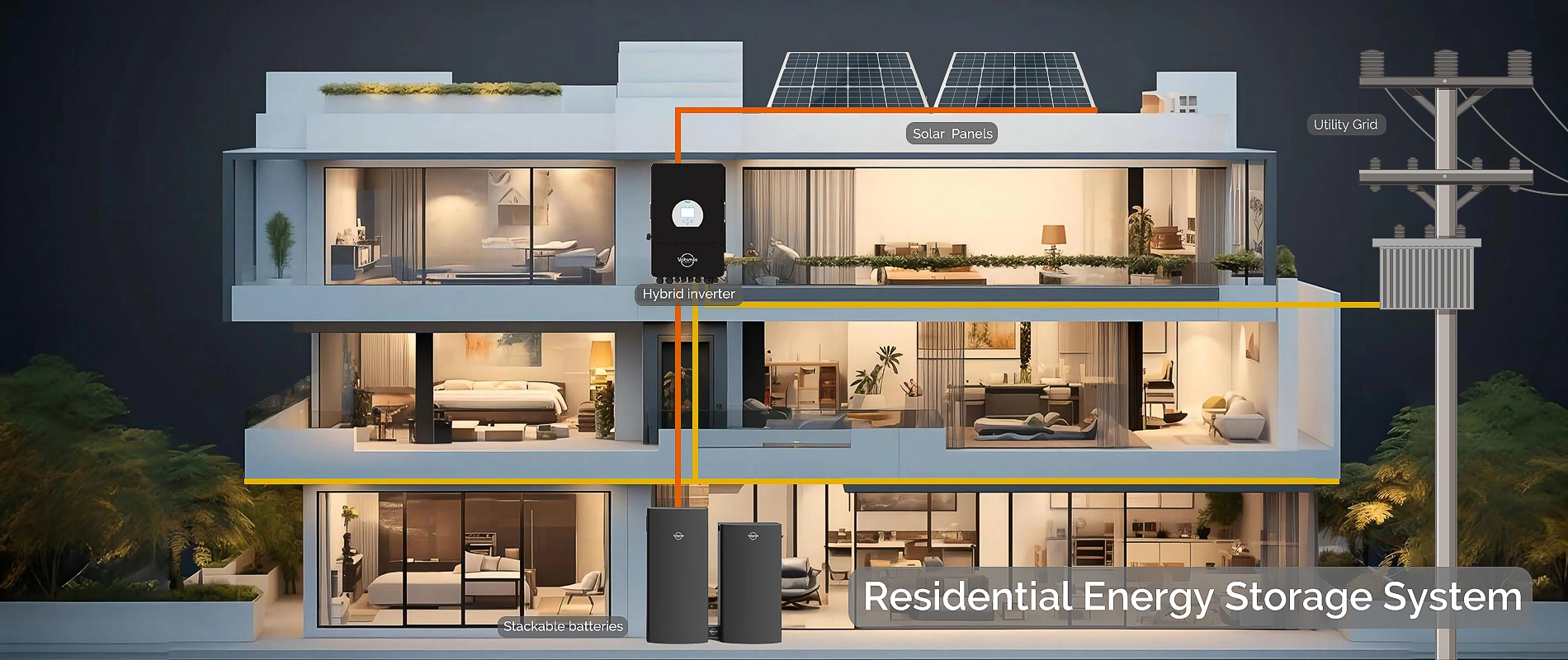
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. How It Works
- Charging: Electrical energy is converted into chemical energy and stored within the battery cells.
- Discharging: The stored chemical energy is converted back into electrical energy when needed.
2. Key Components
- Battery Cells: The core units where energy is stored (e.g., lithium-ion, lead-acid, or flow batteries).
- Battery Management System (BMS): Monitors and controls the charging, discharging, and overall health of the battery.
- Power Conversion System (PCS): Converts stored DC energy into AC for use in homes, businesses, or the grid.
3. Types of Battery Storage
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Widely used for their high energy density, efficiency, and long lifespan.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Cost-effective but with lower energy density and shorter lifespan.
- Flow Batteries: Ideal for large-scale storage due to their scalability and long cycle life.
- Solid-State Batteries: Emerging technology with higher safety and energy density.
4. Applications
- Renewable Energy Integration: Stores excess energy from solar or wind for use during periods of low generation.
- Grid Stabilization: Balances supply and demand, preventing blackouts and improving grid reliability.
- Backup Power: Provides emergency power during outages for homes, businesses, and critical infrastructure.
- Peak Shaving: Reduces energy costs by storing and using energy during off-peak hours during peak demand.
5. Benefits
- Enhances energy efficiency and reduces reliance on fossil fuels.
- Supports the transition to renewable energy by addressing intermittency.
- Improves grid resilience and reduces energy costs for consumers.
6. Challenges
- High upfront costs and limited lifespan of some battery technologies.
- Resource constraints and environmental concerns related to battery production and disposal.
- Technical limitations in energy density and storage capacity.
In summary, battery storage is a versatile and essential technology for modern energy systems, enabling a more sustainable, reliable, and efficient future.
